how can we use biomass energy
How Biomass Is Powering Communities
Biomass is a renewable source of energy that has been gaining popularity in recent years. It refers to organic materials such as plants, wood, and agricultural waste that can be used to produce heat, electricity, and other forms of energy. Biomass power plants are being established in various communities around the world to harness the potential of this sustainable energy source. In this article, we will explore the advantages and impact of biomass power and answer some of the most frequently asked questions regarding this topic.
1. What is biomass power?
Biomass power is the generation of electricity or heat through the combustion or gasification of organic materials. These organic materials can include forestry residues, agricultural waste, energy crops, and even dedicated biomass crops. The energy stored in these materials is released in the form of heat, which is then used to produce steam or drive a turbine to generate electricity.
Image: 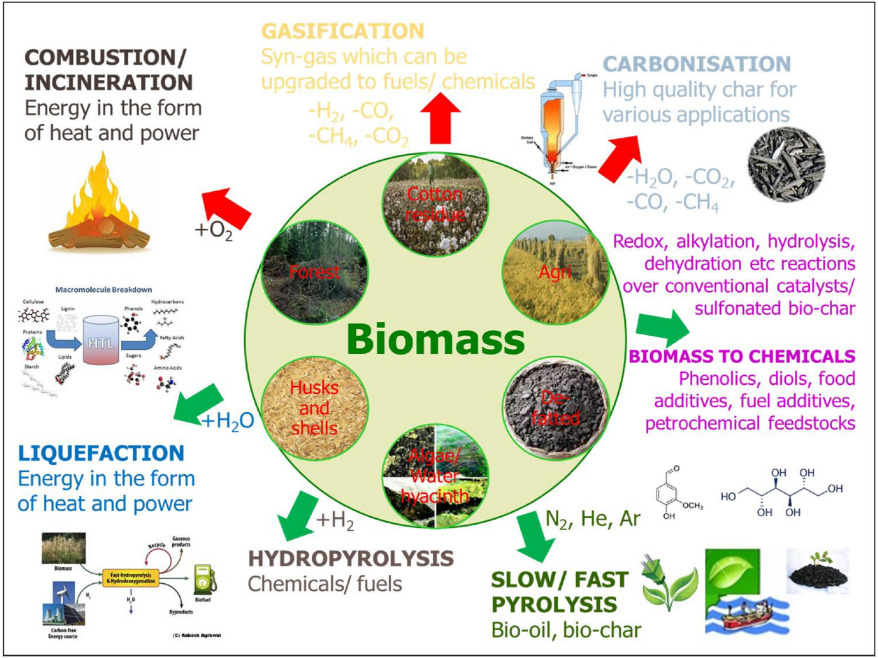
Some key points to consider about biomass power:
- Biomass power is a renewable energy source as organic materials can be replenished.
- It is a carbon-neutral source of energy as the carbon dioxide emitted during combustion is equal to the carbon dioxide absorbed by the plants during their growth.
- Biomass power plants can be tailored to meet the energy needs of a specific community or region.
- Biomass power can contribute to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions and fossil fuel dependency.
2. How does biomass power generation work?
The process of biomass power generation involves several steps:
- Biomass feedstock preparation: The organic material is collected, sorted, and prepared for combustion or gasification.
- Combustion or gasification: The biomass is burned in a boiler or reacted with a controlled amount of oxygen to produce a combustible gas. This gas can then be used to generate heat or electricity.
- Energy conversion: The heat produced by combustion or gasification is used to generate steam, which drives a turbine connected to a generator. This converts the energy of motion into electricity.
- Electricity distribution: The generated electricity is transmitted through a network of power lines to homes, businesses, and other consumers.
Image: 
Some additional information about biomass power generation:
- Biomass power plants can vary in size from small-scale systems that provide heat to a single building to large power plants that supply electricity to the grid.
- Advanced technologies in biomass power generation, such as co-firing with coal or using gasification, can enhance efficiency and reduce emissions.
- Biomass power plants can be integrated with other renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind, to create hybrid energy systems.
3. What are the advantages of biomass power?
Biomass power offers several advantages over conventional energy sources:
- Renewable and sustainable: Biomass is derived from organic materials that can be replenished, making it a renewable source of energy.
- Reduction of greenhouse gas emissions: Biomass power plants release the same amount of carbon dioxide during combustion as the plants absorb during their growth, resulting in near-zero net carbon emissions.
- Waste management: Biomass power generation can utilize agricultural and forestry waste, diverting it from landfills and reducing the environmental impact of disposal.
- Local economic development: Biomass power plants can create employment opportunities and support local economies, especially in rural areas where biomass feedstock is readily available.
Image: 
4. Is biomass power sustainable in the long run?
Yes, biomass power is considered sustainable in the long run. As long as organic materials used for biomass power generation are sourced responsibly and their growth is managed properly, biomass power can be sustained indefinitely. Sustainable practices include ensuring the replenishment and regrowth of biomass feedstock, avoiding the use of unsustainable forestry practices, and implementing efficient and eco-friendly power generation technologies.
It is important to note that biomass power should be a part of a diversified energy mix that includes other renewable and clean energy sources to ensure long-term sustainability and reduce dependence on any single energy source.
5. Can biomass power replace fossil fuels?
While biomass power has the potential to replace some fossil fuel-based energy generation, it is unlikely to completely replace all fossil fuels. Biomass power can certainly contribute to reducing the reliance on fossil fuels and decreasing greenhouse gas emissions. However, a mix of renewable energy sources, including biomass, solar, wind, hydro, and geothermal, is necessary to achieve a sustainable and low-carbon energy future.
Additionally, the availability and suitability of biomass feedstock may vary depending on geographical location, making it more suitable for certain regions than others. The transition to renewable energy should involve a holistic approach that considers the specific energy needs, available resources, and environmental factors of each region or community.
6. Are there any environmental concerns associated with biomass power?
While biomass power is generally considered a sustainable and environmentally friendly source of energy, there are some environmental concerns worth addressing. These concerns include:
- Deforestation: Unsustainable harvesting of biomass feedstock can contribute to deforestation and biodiversity loss. It is crucial to ensure that biomass is sourced from responsibly managed forests and plantations.
- Air emissions: Combustion of biomass can release pollutants such as nitrogen oxides, particulate matter, and volatile organic compounds. However, modern biomass power plants often incorporate advanced emission control technologies to minimize these impacts.
- Water usage: Biomass power plants may require water for cooling purposes or in the steam generation process. Implementing water-efficient technologies and proper wastewater management is essential to minimize water consumption and prevent water pollution.
Addressing these concerns requires adherence to sustainability standards, implementing appropriate mitigation measures, and adopting continuous improvements in biomass power generation technologies.
7. How does biogas contribute to biomass power?
Biogas is a byproduct of the anaerobic digestion or fermentation of organic materials such as agricultural waste, food waste, and sewage sludge. It is a mixture of methane, carbon dioxide, and trace amounts of other gases. Biogas can be utilized as a renewable energy source for heating, electricity generation, or transportation fuel.
In the context of biomass power, biogas can be a valuable component. It can be combusted to produce heat, which can be used directly or converted into electricity. Biogas can also be purified to remove impurities and upgraded to biomethane, which has similar properties to natural gas and can be injected into the natural gas grid or used as a transportation fuel.
Image: 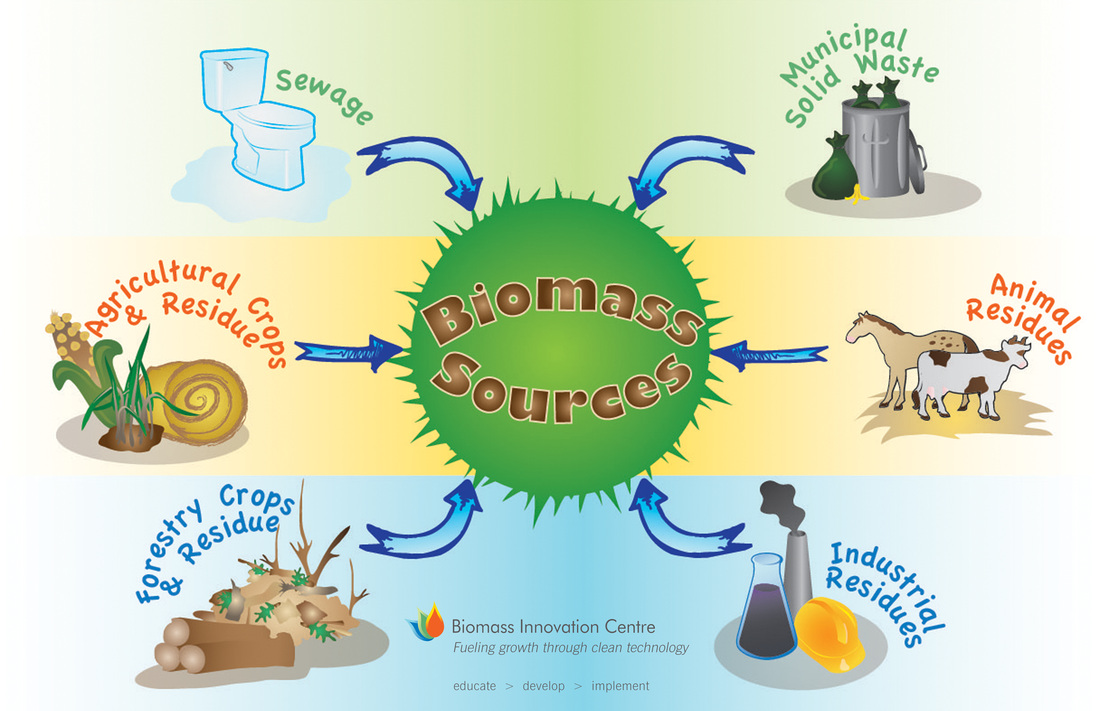
Some advantages of biogas in biomass power generation include:
- Utilization of organic waste: Biogas can be generated from various organic waste sources, providing an environmentally friendly way to manage waste while producing energy.
- Reduction of emissions: Biogas combustion releases less carbon dioxide and other pollutants compared to fossil fuel combustion, leading to lower greenhouse gas emissions and environmental impact.
- Localized energy production: Biogas can be produced on-site at farms, wastewater treatment plants, or other waste facilities, enabling localized energy production and reducing the need for long-distance transportation of fossil fuels.
8. What are the challenges of biomass power?
Despite its many advantages, biomass power also faces certain challenges that need to be addressed:
- Availability and logistics: Ensuring a sustainable and consistent supply of biomass feedstock can be challenging, as it depends on factors such as seasonal variations, land availability, and transportation logistics. Proper planning and coordination are crucial.
- Technology and efficiency: Biomass power plants require advanced technologies that maximize energy conversion efficiency, minimize emissions, and ensure proper waste management. Continuous research and development efforts are essential to optimize plant performance.
- Public acceptance: Biomass power plants often face opposition from local communities due to concerns about air emissions, noise, and odor. Effective communication, public engagement, and adherence to strict environmental standards can help address these concerns.
Overcoming these challenges requires collaborations between policymakers, industry stakeholders, and local communities to develop sustainable biomass supply chains, promote technological advancements, and build public trust.
9. Can biomass power be used in residential properties?
Although biomass power is more commonly associated with larger-scale power plants, it can also be utilized in residential properties, especially in rural areas. Small-scale biomass boilers or stoves can provide heating and hot water by burning wood pellets, agricultural waste, or dedicated biomass fuels.
Residential biomass power has the following benefits:
- Energy independence: By generating heat or electricity from biomass on-site, residential properties can reduce their reliance on traditional grid electricity or fossil fuel-based heating systems.
- Cost savings: Biomass fuels can often be more cost-effective compared to fossil fuels, resulting in potential long-term savings on energy bills.
- Environmental sustainability: Using biomass for residential power can help reduce carbon emissions and contribute to a more sustainable energy system.
10. Are there any subsidies or incentives for biomass power projects?
Many countries and regions have implemented subsidies, incentives, and support mechanisms to promote the development of biomass power projects. These measures aim to accelerate the transition towards renewable energy sources and achieve various energy and climate goals.
The specific subsidies and incentives vary depending on the jurisdiction and may include:
- Feed-in tariffs: Guaranteed payments or premium prices for renewable electricity generated from biomass
- Renewable energy certificates: Tradable instruments representing the environmental attributes of renewable energy
- Tax credits or deductions: Financial incentives to reduce the tax burden for biomass power project developers or operators
- Grants and funding programs: Direct funding or grants provided by governments or organizations to support biomass power projects
These subsidies and incentives aim to make biomass power more economically viable, attractive to investors, and competitive with conventional energy sources. However, it is essential to ensure that such support mechanisms are designed and implemented in a way that promotes sustainable biomass sourcing, efficient technology deployment, and overall environmental benefits.
11. Can biomass power contribute to achieving climate change targets?
Yes, biomass power has the potential to contribute significantly to climate change targets and global efforts to mitigate greenhouse gas emissions. By displacing fossil fuel-based energy generation, biomass power can help reduce carbon dioxide emissions.
Some ways in which biomass power can contribute to climate change mitigation include:
- Carbon neutrality: Biomass power produces carbon dioxide emissions during combustion, but these emissions are part of the natural carbon cycle. The carbon dioxide released by burning biomass is equivalent to the carbon dioxide absorbed during the growing process, resulting in near-zero net emissions.
- Substitution of fossil fuels: Biomass power allows for the substitution of coal, oil, or natural gas in power generation, reducing the emissions associated with these fossil fuels.
- Potential for carbon capture and storage (CCS): Biomass power plants can potentially integrate CCS technologies, capturing and permanently storing carbon dioxide emissions. This can further enhance the climate change mitigation potential of biomass power.
12. How can communities benefit from biomass power?
Communities can benefit from biomass power in various ways, including:
- Job creation: Biomass power plants require personnel for operations, maintenance, and administration, contributing to local employment opportunities.
- Economic development: Biomass power projects can stimulate economic activity in rural areas by utilizing locally available biomass feedstock, attracting investments, and supporting local businesses.
- Energy security: Biomass power can enhance a community's energy security by diversifying the energy mix, reducing dependence on fossil fuel imports, and promoting local energy production.
- Sustainable waste management: Biomass power generation provides a sustainable solution for managing organic waste and residues, reducing landfill usage, and minimizing environmental impacts.
Additionally, biomass power plants can serve as educational and research centers, partnering with academic institutions and community organizations to promote knowledge sharing, vocational training, and innovation in the renewable energy sector.
In conclusion, biomass power is a renewable and sustainable energy source that has the potential to power communities and contribute to global efforts in mitigating climate change. It offers advantages such as carbon neutrality, waste management, and local economic development. However, challenges such as biomass availability, technology advancement, and public acceptance need to be addressed for the widespread adoption of biomass power. By fostering a supportive policy environment, promoting research and development, and engaging local communities, biomass power can play a significant role in the transition to a clean and sustainable energy future.