how do we get energy from biomass
Energy Transitions Commission warns demand for biomass likely to exceed

1. Is biomass a sustainable energy source?
Biomass is generally considered a sustainable energy source. It involves using organic materials, such as plant matter and agricultural waste, to generate energy. This process helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions as the carbon dioxide released during energy production is balanced by the carbon absorbed during the growth of the biomass. It is important, however, to ensure responsible sourcing and management practices to maintain the sustainability of biomass energy.
- Biomass is a renewable energy source as it relies on organic materials that can be regrown.
- It can provide a consistent and reliable source of energy.
- Biomass energy can contribute to reducing reliance on fossil fuels and mitigating climate change.
2. What are the benefits of using biomass energy?
There are several benefits associated with using biomass energy:
- It helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions and combat climate change.
- Biomass energy utilizes organic waste materials, which can help in waste management.
- It supports local economies by creating job opportunities in biomass production and processing.
- Biomass can be produced domestically, reducing dependence on imported fossil fuels.
- It provides a versatile energy source that can be used for heating, electricity generation, and transportation.
3. How does biomass energy contribute to sustainable development?
Biomass energy plays a crucial role in sustainable development by:
- Reducing reliance on fossil fuels and promoting the use of renewable energy sources.
- Supporting the transition to a low-carbon economy and achieving climate change goals.
- Providing opportunities for rural development and creating jobs in the biomass sector.
- Encouraging sustainable land use practices and responsible forestry management.
4. What are the challenges of using biomass energy?
While biomass energy has numerous advantages, it also faces certain challenges:
- Availability and accessibility of biomass feedstock can vary depending on geographical location.
- Efficient collection, transportation, and storage of biomass can be logistically challenging.
- Competition with other sectors for biomass resources, such as food production or soil fertility.
- Ensuring the sustainability and responsible sourcing of biomass feedstock.
- Addressing potential environmental impacts, such as emissions from biomass combustion.
5. How can the demand for biomass energy be met sustainably?
To meet the demand for biomass energy sustainably, it is important to:
- Promote responsible and sustainable biomass production practices, including the use of waste materials and dedicated energy crops.
- Implement efficient logistics systems for biomass collection, transportation, and storage.
- Encourage research and development to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of biomass energy technologies.
- Ensure strict adherence to sustainability criteria and certifications in biomass sourcing.
- Invest in renewable energy infrastructure to support the integration of biomass energy into the energy mix.
6. Can biomass energy be used on a large scale?
Yes, biomass energy can be used on a large scale. It is already being utilized in various countries for electricity generation, heating, and industrial processes. However, the scalability of biomass energy depends on the availability of biomass feedstock and the infrastructure required for its conversion and utilization. Large-scale implementation requires careful planning, sustainable sourcing, and supportive policies.
7. Is biomass energy more environmentally friendly than fossil fuels?
Biomass energy is generally considered more environmentally friendly than fossil fuels due to its renewable nature and lower carbon emissions. When biomass is burned, it releases carbon dioxide, but this is offset by the carbon absorbed during the growth of biomass feedstock. Fossil fuels, on the other hand, release carbon dioxide that has been trapped underground for millions of years, contributing to the greenhouse effect and climate change.
- Biomass energy helps mitigate climate change by reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
- It promotes the use of renewable energy sources instead of non-renewable fossil fuels.
- Using biomass can help decrease air pollution compared to burning fossil fuels.
8. What role can biomass energy play in reducing carbon emissions?
Biomass energy can play a significant role in reducing carbon emissions:
- Burning biomass releases CO2, but this is part of the natural carbon cycle, unlike the combustion of fossil fuels.
- Biomass plants can be designed with carbon capture and storage (CCS) technologies to further reduce CO2 emissions.
- Switching from fossil fuel-based power plants to biomass power plants can lead to substantial emissions reductions.
- Using sustainable biomass feedstock helps avoid the release of fossil carbon and encourages carbon sequestration in plants.
9. Is biomass energy economically viable?
Biomass energy can be economically viable under certain conditions:
- The availability and affordability of biomass feedstock.
- Investment in efficient biomass conversion technologies.
- Policies and incentives that support renewable energy and biomass utilization.
- Integration of biomass energy into existing energy systems and grids.
- Evaluation of the full life cycle costs and benefits of biomass energy compared to other energy sources.
10. How can biomass energy contribute to rural development?
Biomass energy can contribute to rural development in various ways:
- Creation of jobs in biomass production, processing, and supply chain management.
- Providing opportunities for local farmers and communities to participate in renewable energy production.
- Supporting sustainable agriculture practices by utilizing crop residues and waste materials for biomass energy.
- Reducing reliance on imported fossil fuels and promoting energy independence in rural areas.
11. What are the social benefits of biomass energy?
The social benefits of biomass energy include:
- Creating employment opportunities and contributing to local economies.
- Improving access to clean and affordable energy in rural areas.
- Reducing energy poverty and increasing energy resilience.
- Empowering communities to participate in renewable energy production and decision-making processes.
12. What are the different forms of biomass used for energy production?
The different forms of biomass used for energy production include:
- Wood and wood pellets obtained from forestry and timber industries.
- Agricultural residues, such as corn stover, straw, and sugarcane bagasse.
- Energy crops, including switchgrass, miscanthus, and fast-growing trees.
- Biogas produced from organic waste materials through anaerobic digestion.
- Algae biomass cultivated for biofuels and other energy applications.
Reasons Why Biomass Energy Should Be a Top Choice - REURASIA
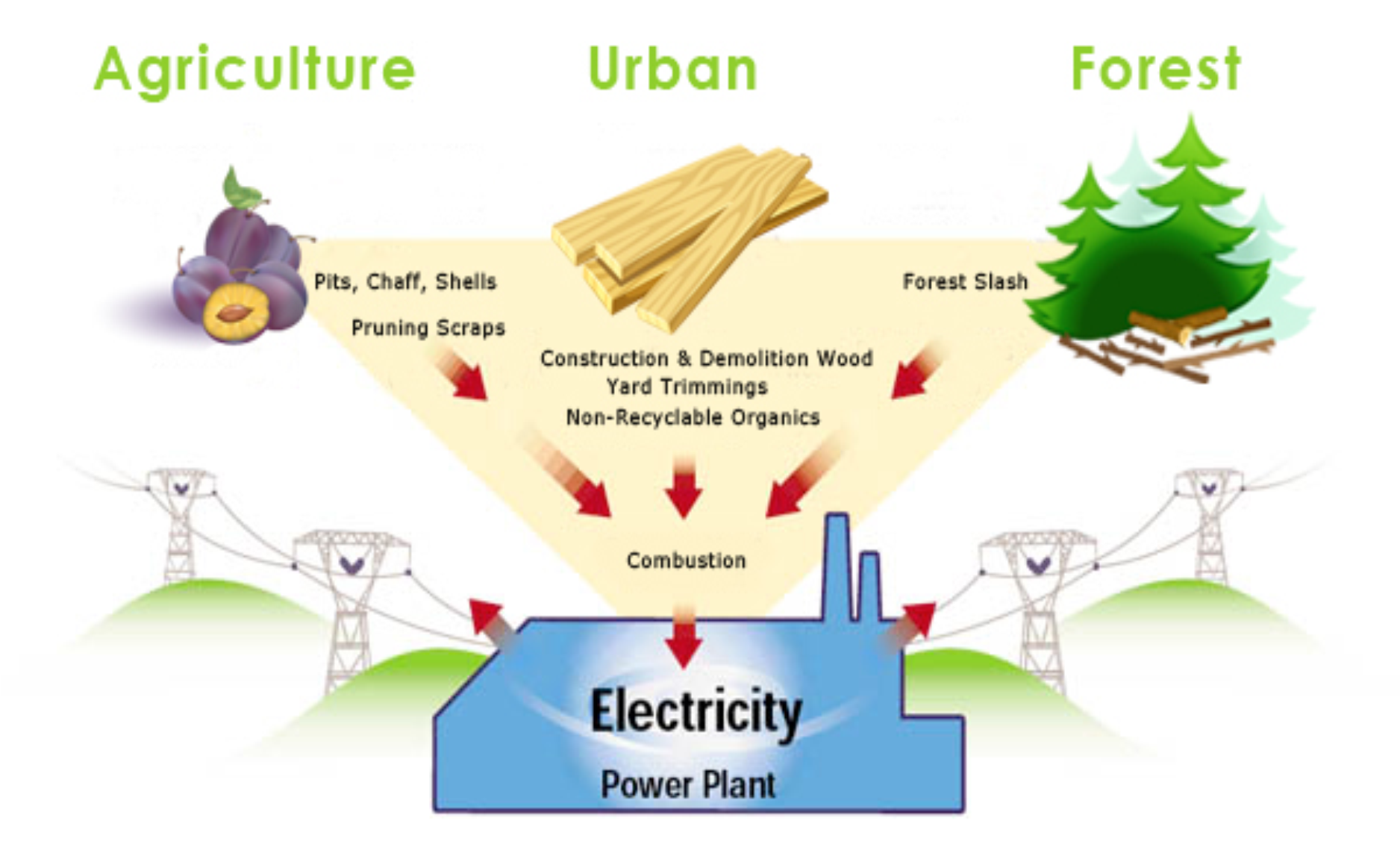
1. What makes biomass energy a top choice?
Biomass energy is considered a top choice for several reasons:
- It is a renewable energy source that reduces greenhouse gas emissions.
- Biomass can be locally produced, enhancing energy security and independence.
- It provides a reliable and consistent energy supply, especially for heat and electricity generation.
- Biomass utilization supports waste management and encourages sustainable land use practices.
2. How does biomass energy contribute to a sustainable future?
Biomass energy contributes to a sustainable future by:
- Reducing reliance on fossil fuels and mitigating climate change.
- Promoting the use of renewable energy sources and supporting sustainable development.
- Encouraging responsible sourcing and management of biomass feedstock.
- Creating economic opportunities and benefiting local communities.
3. Can biomass energy replace fossil fuels entirely?
Biomass energy has the potential to replace a significant portion of fossil fuels. However, a complete replacement may be challenging due to:
- Technological limitations in terms of energy density and efficiency.
- The need for sustainable biomass feedstock sources.
- The requirement for complementary renewable energy sources to meet all energy demands.
While biomass energy can play a substantial role in reducing fossil fuel dependence, a diversified energy mix is often recommended for energy security and resilience.
4. Is biomass energy expensive to produce?
The cost of biomass energy production can vary depending on various factors:
- The availability and accessibility of biomass feedstock.
- The efficiency of biomass conversion technologies.
- The scale of biomass energy production and infrastructure.
- Policies, incentives, and market conditions supporting biomass utilization.
- The evaluation of life cycle costs, including feedstock production, transportation, and conversion.
While biomass energy production costs can be competitive with other renewable energy sources, continued investments in research and technological advancements can further enhance cost-effectiveness.
5. Can biomass energy be used for transportation?
Yes, biomass energy can be used for transportation through different means:
- Biofuels derived from biomass, such as ethanol and biodiesel, can be used as alternatives to conventional fossil fuels.
- Biomass-based electricity can power electric vehicles and automotive systems.
- Advanced conversion technologies, like biomass gasification, can produce synthesis gases for hydrogen fuel cells.
Biomass energy offers opportunities to decarbonize the transport sector and reduce greenhouse gas emissions associated with fossil fuel use.
6. What are the potential environmental impacts of biomass energy?
Biomass energy production can have both positive and negative environmental impacts:
- Positive impacts include reduced greenhouse gas emissions and the utilization of organic waste materials.
- Negative impacts may arise from unsustainable biomass sourcing, land-use change, and emissions from incomplete combustion.
- Environmental safeguards and sustainable practices, such as sustainable sourcing guidelines and emissions control technologies, can mitigate potential negative impacts.
Regular monitoring and assessment of the environmental performance of biomass energy projects are essential for minimizing environmental risks and ensuring sustainability.
7. Can biomass energy be integrated into existing energy systems?
Biomass energy can be integrated into existing energy systems through:
- Co-firing biomass with coal in existing power plants, reducing the carbon intensity of electricity generation.
- Upgrading biomass systems to supply heat or combined heat and power (CHP) to industrial processes.
- Utilizing biomass for district heating systems in urban areas.
- Integrating biomass-based electricity generation into the grid alongside other renewable energy sources.
Effective integration requires appropriate infrastructure, grid compatibility, and supportive policies.
8. How does biomass energy contribute to waste management?
Biomass energy contributes to waste management by:
- Using organic waste materials, such as agricultural residues and food waste, as biomass feedstock.
- Reducing the volume of waste sent to landfills or incineration facilities.
- Minimizing methane emissions from decomposing organic waste.
- Creating valuable energy resources from otherwise discarded materials.
9. What role does biomass energy play in reducing air pollution?
Biomass energy can help reduce air pollution through:
- Substituting fossil fuel-based energy sources with cleaner biomass-based alternatives.
- Decreasing emissions of sulfur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and particulate matter.
- Utilizing emission control technologies in biomass combustion processes.
- Promoting sustainable land use practices and reducing the impact of agricultural burning.
10. Can biomass energy support rural electrification?
Yes, biomass energy can support rural electrification by:
- Providing a localized and decentralized energy supply for remote communities.
- Utilizing locally available biomass feedstock resources.
- Creating job opportunities and economic development in rural areas.
- Delivering reliable and affordable electricity to underserved regions.
11. How does biomass energy contribute to energy diversification?
Biomass energy contributes to energy diversification by:
- Expanding the range of available renewable energy sources alongside wind, solar, and hydro power.
- Reducing dependence on imported fossil fuels and promoting domestic energy production.
- Enhancing energy security and resilience through diversified energy portfolios.
- Providing additional flexibility in the energy mix for balancing intermittent renewable sources.
12. What are the considerations for sustainable biomass sourcing?
Sustainable biomass sourcing requires careful considerations:
- Promoting responsible land-use practices, including sustainable forestry management.
- Preventing deforestation and protecting biodiversity.
- Ensuring the availability and viability of biomass feedstock sources.
- Adhering to sustainability standards, certifications, and transparent supply chain systems.
Collaboration between stakeholders, such as government agencies, biomass producers, and environmental organizations, is crucial for establishing sustainable biomass sourcing practices.